How can aquifers become depleted or contaminated?
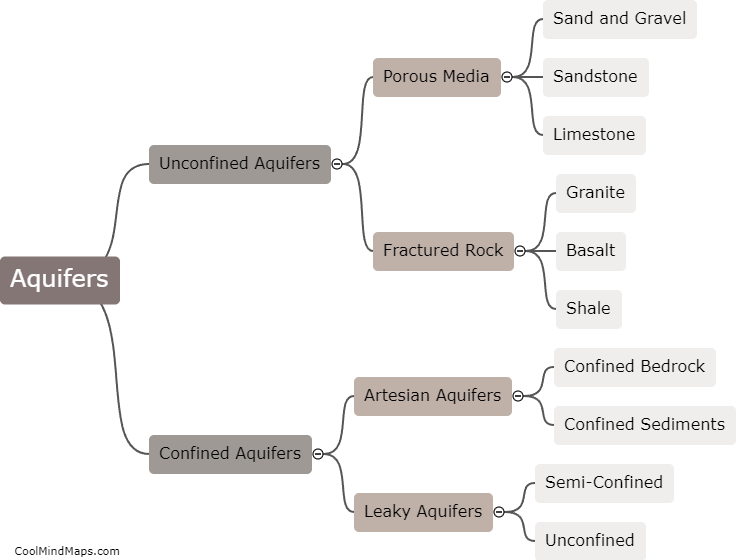
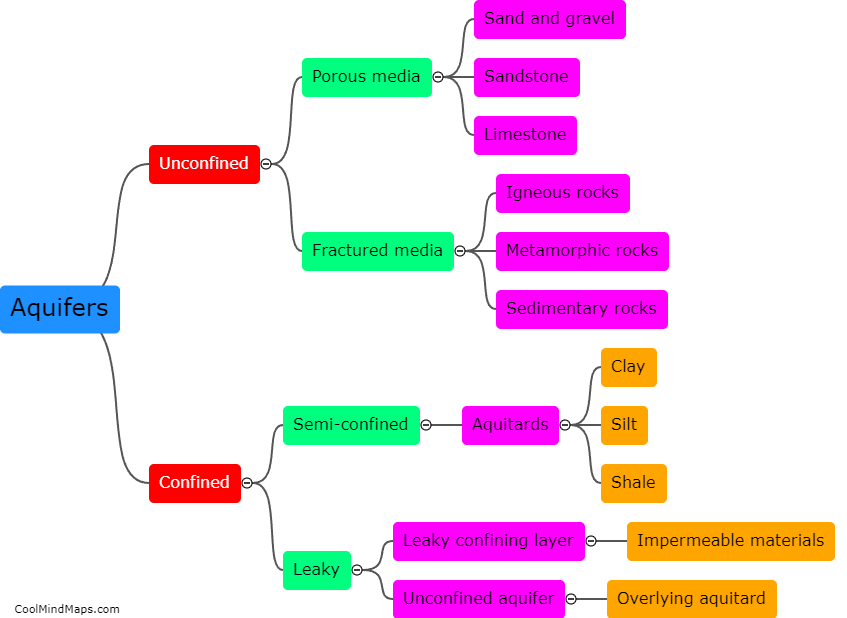
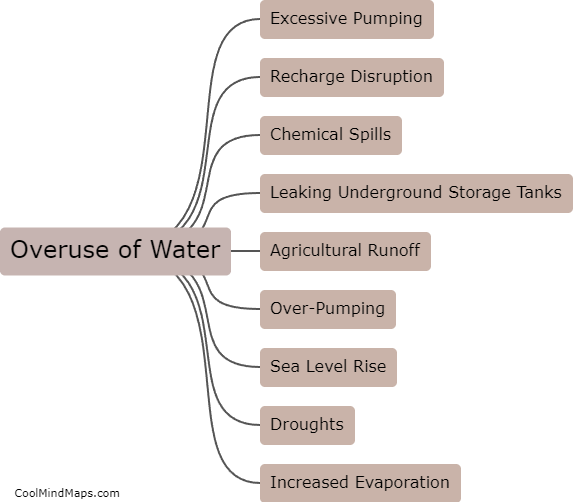
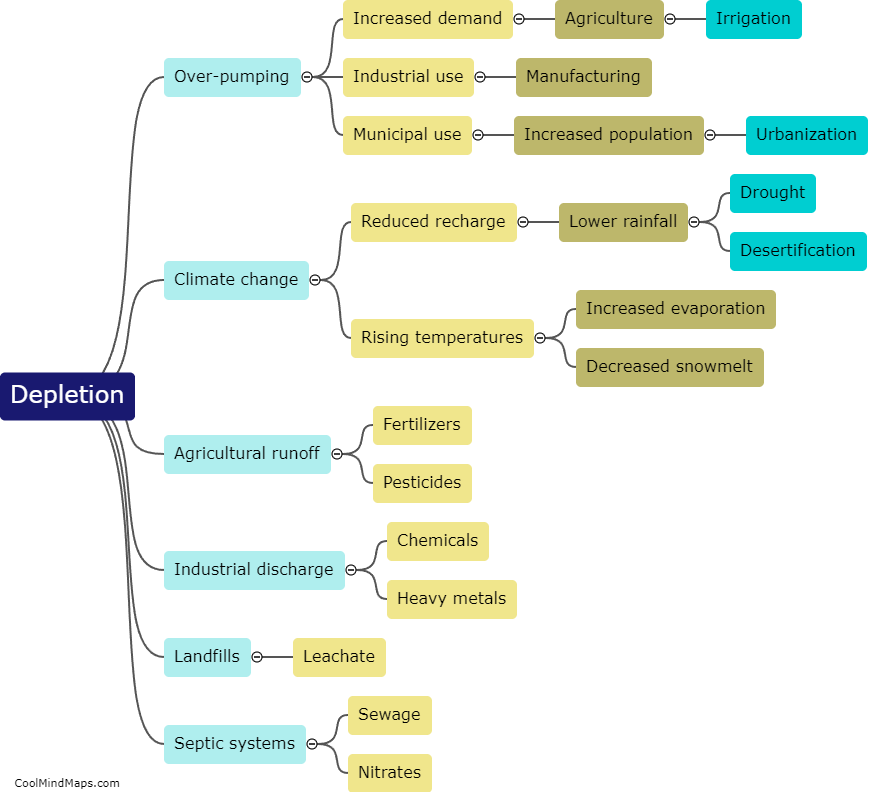
Aquifers, which are underground layers of water-bearing rock or sediment, can become depleted or contaminated due to various factors. Over-pumping for irrigation, industrial use, or public water supply can lead to the depletion of aquifers. When the rate of water extraction exceeds the rate of natural recharge, the aquifer can gradually lose its ability to replenish itself adequately. Additionally, contamination can occur when pollutants from human activities, such as chemical spills, improper waste disposal, or agricultural practices, seep into the groundwater, rendering it unsafe for consumption. Contamination can also arise from natural sources like geological formations or the intrusion of saltwater into coastal aquifers. The consequences of aquifer depletion or contamination can be detrimental for both the environment and human health, underscoring the need for efficient management and protection of these crucial water sources.
This mind map was published on 27 November 2023 and has been viewed 59 times.