How is idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis diagnosed?
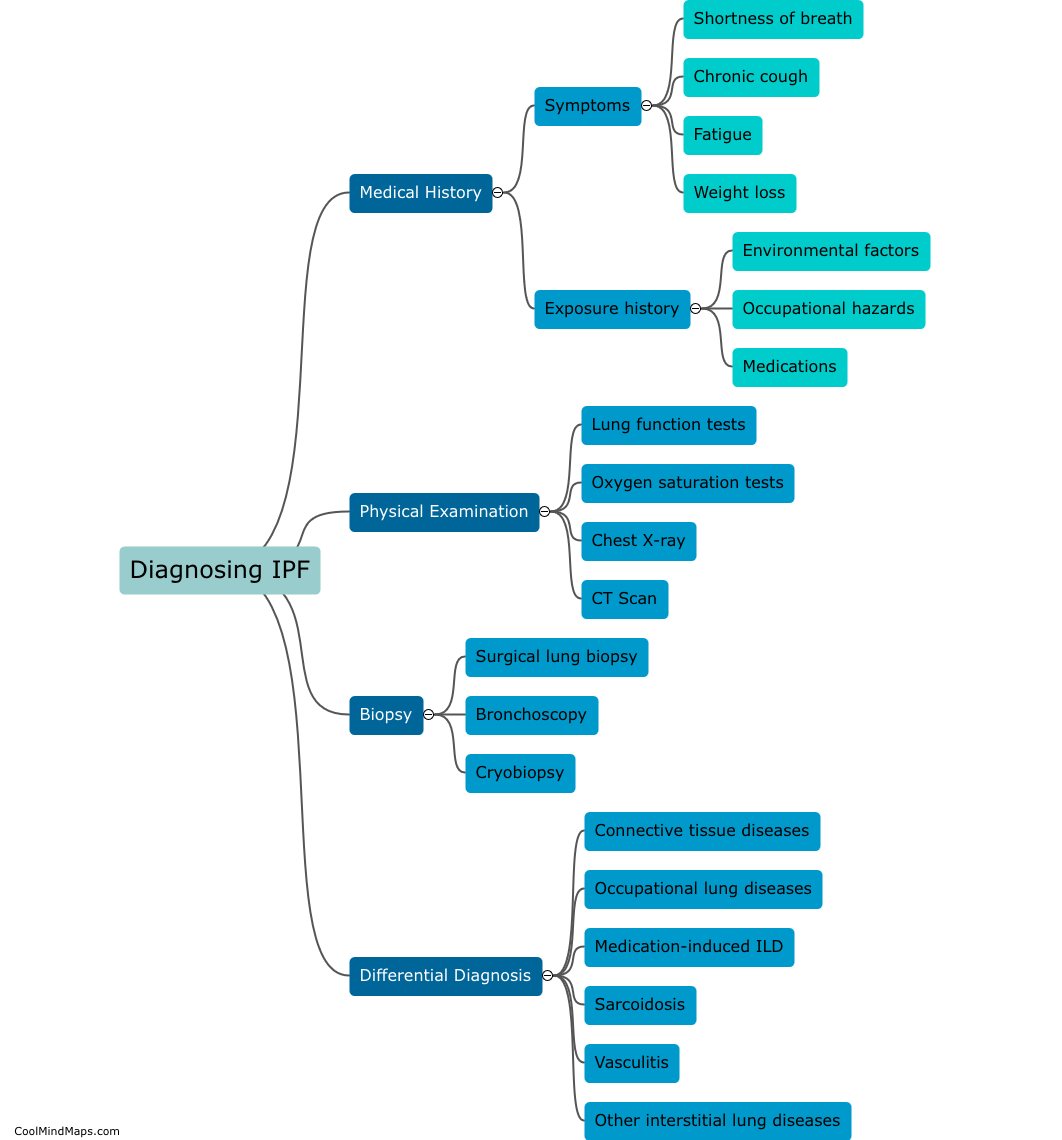
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) is usually diagnosed through a combination of medical history, physical examination, imaging studies (including high-resolution computed tomography), and pulmonary function tests. Additionally, a lung biopsy may be necessary to confirm the diagnosis and rule out other potential causes. Clinicians may use a scoring system known as the GAP index to assess the severity of IPF, and patients may be referred to a pulmonologist or other specialist for further evaluation and treatment. Overall, prompt and accurate diagnosis of IPF is essential for enabling appropriate management and improving patient outcomes.
This mind map was published on 16 May 2023 and has been viewed 85 times.